Semiconductor Today, September 25th, 2013
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE in Freiburg, Germany, concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) system maker Soitec of Bernin, France, micro/nanotechnology R&D center CEA-Leti in Grenoble, France and the Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin have jointly achieved a new record for solar energy conversion efficiency by using a new cell structure with four subcells.
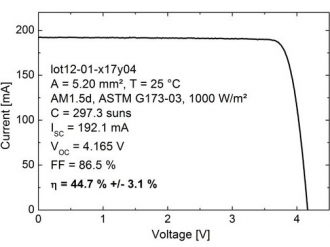
Previously, in May, the German-French team reported a four-junction solar cell with 43.6% efficiency, while Solar Junction Corp of San Jose, CA, USA reported a 44.1%-efficient production-ready cell in August following Sharp in June reporting a 44.4%-efficient triple-junction cell in research. After just over three years of research on the four-junction solar cell, the the German-French team’s new record of 44.7% was measured at a concentration of 297 suns. The latest figure is cited as a major step on the roadmap towards 50% efficiency.
“Besides improved materials and optimization of the structure, a new procedure called wafer bonding plays a central role,“ says Frank Dimroth, department head & project leader in charge of the development work at Fraunhofer ISE. “With this technology, we are able to connect two semiconductor crystals, which otherwise cannot be grown on top of each other with high crystal quality. In this way we can produce the optimal semiconductor combination to create the highest efficiency solar cells,” he adds.